Micronutrient Profile of a Cutie

Nutrition facts of a cutie – Cuties, also known as mandarin oranges, are small, sweet citrus fruits packed with essential vitamins and minerals. Their nutritional profile contributes significantly to a healthy diet, offering a convenient and delicious way to boost your intake of several micronutrients. This section will detail the specific vitamin and mineral content of cuties, and compare it to other popular citrus fruits.
Vitamin Content of Cuties
Cuties are an excellent source of Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant crucial for immune function, collagen production, and iron absorption. A single cutie typically provides a significant portion of the recommended daily intake of Vitamin C. Beyond Vitamin C, cuties also contain smaller amounts of other B vitamins, such as thiamin, riboflavin, and niacin, which play vital roles in energy metabolism and various bodily functions.
While not as abundant as Vitamin C, these B vitamins contribute to the overall nutritional value of the fruit.
Mineral Content of Cuties
Cuties are a good source of potassium, an essential mineral that helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance within the body. They also contain smaller amounts of other minerals, including magnesium and calcium, both important for bone health and various metabolic processes. The mineral content, while not as prominent as the vitamin content, adds to the overall nutritional benefits of consuming cuties.
Comparison of Micronutrient Content to Other Citrus Fruits, Nutrition facts of a cutie
Compared to other citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits, cuties generally have a similar or slightly lower Vitamin C content per serving. However, the ease of peeling and consuming a cutie often makes it a more convenient choice for snacking, potentially leading to higher overall Vitamin C intake compared to other citrus fruits that require more preparation. The mineral content of cuties is comparable to other citrus fruits, with potassium being a commonality across the group.
The specific nutrient profiles vary slightly depending on factors such as growing conditions and variety.
Micronutrient Summary of Cuties
- Vitamin C: Excellent source; contributes significantly to daily recommended intake. Supports immune function and collagen production.
- Vitamin B (Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin): Present in smaller amounts; contributes to energy metabolism and various bodily functions.
- Potassium: Good source; important for blood pressure regulation and fluid balance.
- Magnesium and Calcium: Present in smaller amounts; contributes to bone health and various metabolic processes.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While cuties offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, it’s important to acknowledge potential drawbacks and considerations for certain individuals. The naturally occurring sugars and potential for allergic reactions, as well as interactions with specific medications or health conditions, warrant attention.While cuties are a good source of Vitamin C and other nutrients, their sugar content should be considered, particularly for individuals managing blood sugar levels.
A single cutie contains a moderate amount of natural sugars, which can contribute to overall daily sugar intake. For people with diabetes or those monitoring their carbohydrate consumption, incorporating cuties into their diet requires careful planning and portion control. For example, someone on a strict diabetic diet might need to adjust their insulin dosage or other medications if they consume a large quantity of cuties.
Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels after cutie consumption is advisable for individuals with diabetes.
Sugar Content and Blood Sugar Management
The natural sugars in cuties, primarily fructose and glucose, can impact blood sugar levels. Individuals with diabetes or those managing their blood sugar should monitor their intake and consider the overall carbohydrate content of their diet. Portion control is key; consuming several cuties in one sitting could lead to a significant spike in blood sugar. Consulting a doctor or registered dietitian is recommended for personalized guidance on incorporating cuties into a diabetes management plan.
For instance, a person with type 1 diabetes might find that consuming one cutie as part of a balanced meal, alongside protein and healthy fats, has a less dramatic impact on their blood sugar than consuming several cuties on an empty stomach.
Allergic Reactions
Although rare, allergic reactions to citrus fruits, including cuties, are possible. These reactions can range from mild symptoms like skin rashes or itching to more severe reactions such as anaphylaxis, which requires immediate medical attention. Individuals with a known citrus allergy should avoid consuming cuties. Symptoms of a citrus allergy might include hives, swelling of the lips or tongue, difficulty breathing, or a sudden drop in blood pressure.
Understanding the nutritional profile of a cutie fruit, often overlooked, is surprisingly insightful. For a comparative perspective on lean protein sources, it’s helpful to examine the nutritional data available for other foods like meat; for instance, you can check out detailed information on pork chops nutrition facts to contrast the macronutrient composition. Returning to our cutie fruit, remember that its nutritional value lies in its vitamin C and fiber content, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
If any of these symptoms occur after consuming a cutie, seek immediate medical attention.
Interactions with Medications and Health Conditions
Certain medications and health conditions may necessitate caution when consuming cuties. For example, some medications can interact with the vitamin K content in cuties, potentially affecting blood clotting. Individuals taking blood thinners should consult their doctor before significantly altering their citrus fruit intake. Additionally, people with gastrointestinal issues like acid reflux might experience discomfort after consuming acidic fruits like cuties.
In such cases, consuming cuties in moderation or after meals might be beneficial. The high Vitamin C content in cuties could also potentially interfere with the absorption of certain medications; again, consulting a physician is advisable to assess any potential risks based on individual circumstances and medications.
Visual Representation of Nutritional Information: Nutrition Facts Of A Cutie
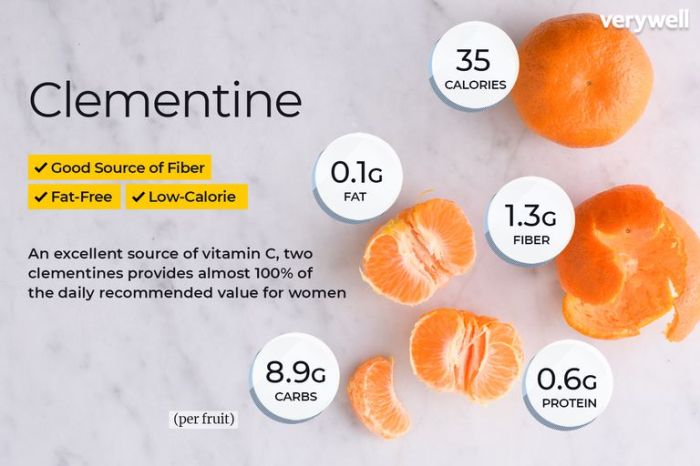
Understanding the nutritional content of a cutie is easier when visualized. This section provides descriptive representations to help grasp serving sizes and macronutrient proportions. Clear visuals aid in understanding the nutritional value within the context of portion size.
Cutie Size and Texture
Imagine a small, roughly spherical citrus fruit, approximately 2-3 inches in diameter. Its skin is a vibrant, deep orange, sometimes with a slight blush of red, depending on the variety and ripeness. The texture of the skin is slightly bumpy, not smooth, with small, visible pores. Inside, the fruit is segmented into roughly 8-10 sections, each filled with juicy, slightly acidic flesh.
The flesh is a lighter orange than the skin, with a soft, somewhat tender texture, but not overly soft or mushy. A single cutie generally constitutes a single serving.
Macronutrient Proportion Visualization
To represent the macronutrient composition of a single cutie, consider a simple pie chart. The chart is divided into three sections representing carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The largest section, representing carbohydrates, is a light golden-yellow, occupying approximately 75% of the pie chart. This reflects the relatively high carbohydrate content of a cutie. A small, pale yellow section, approximately 15%, represents the fat content.
Finally, a tiny sliver, approximately 10%, representing protein, is depicted in a pale orange. The colors are chosen to be visually distinct and representative of the respective macronutrients; the sizes are proportionate to their approximate percentage contributions in a typical cutie. This visual representation provides a quick and intuitive understanding of the relative proportions of macronutrients present.
Essential FAQs
Are all “cuties” nutritionally identical?
No. Nutritional content can vary slightly depending on the specific variety of mandarin orange and growing conditions.
Can I eat cuties if I have diabetes?
Individuals with diabetes should consume cuties in moderation due to their sugar content and monitor their blood glucose levels accordingly. Consult with a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized advice.
Are there any known interactions between cuties and medications?
While generally safe, there’s no documented significant interaction between cuties and common medications. However, individuals with specific health conditions or those on medication should consult their doctor or pharmacist for any potential concerns.
How many cuties should I eat per day?
The recommended daily intake depends on individual dietary needs and overall calorie goals. One to two cuties per day could be a reasonable addition to a balanced diet for most adults.
What are some creative ways to use cuties beyond eating them whole?
Cuties can be added to salads, incorporated into salsas, used in desserts, or juiced for a refreshing drink.
